
Additive manufacturing, or popularly known as 3D printing, is shaping a wide range of products across various sectors. We are witnessing a paradigm shift in how products are being manufactured. The traditional manufacturing process is being utilized less, while a rapid manufacturing process powered by an imaginative level of design freedom is gaining traction among businesses.
The footwear sector is also seeing the new disruption. Growing more and more in popularity, 3D printing presents unlimited potential for the industry. Let’s take a look at how 3D printing is already changing the way footwear is manufactured.
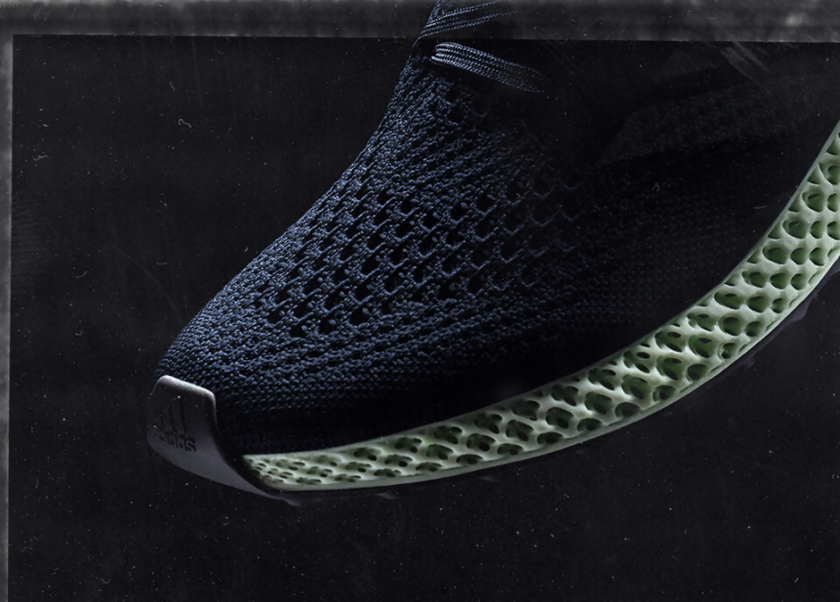
Adidas Futurecraft 4D

Source: Adidas
Adidas, the sports equipment manufacturing giant, partnered with Silicon Valley’s most popular manufacturing startup, Carbon, to manufacture a 3D printed footwear series – the Futurecraft 4D. This range is a marvel in itself particularly due to the complex midsole structure made possible Carbon’s proprietary 3D printing technology called Digital Light Synthesis™ (DLS).
The midsole of Futurecraft 4D is a groundbreaking innovation in itself. The lattice structured midsole not only meets the performance parameters but also accords comfort to the users. The design allows Adidas to provide bespoke athletic footwear by altering the cushioning properties throughout the shoe.
The technology has allowed Adidas to use its vast set of biomechanical data to rapidly convert the data directly into a customized shoe for the athlete. A level of customization never reached before for a volume produced by Adidas.
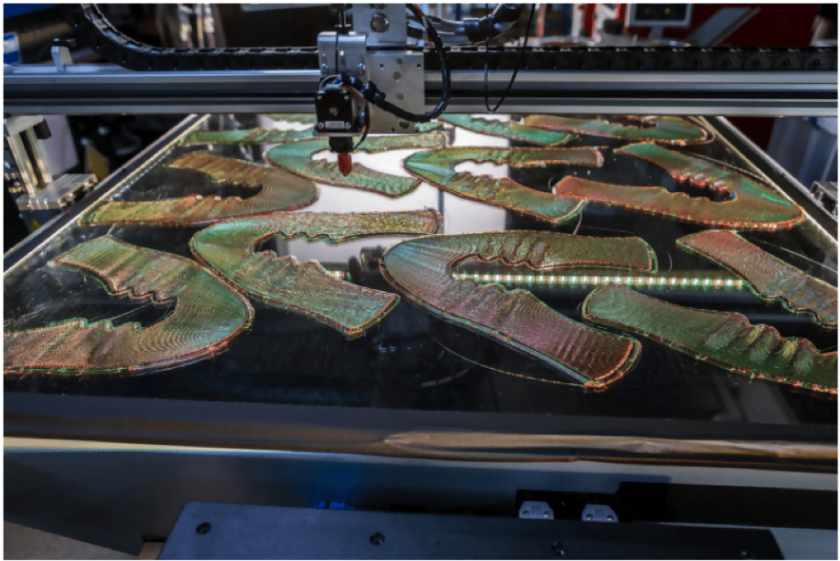
Nike Flyprint
Source: Nike
A typical shoe consists of three parts: Sole, Midsole and the upper Fabric. While Adidas has concentrated on 3D printing the midsole, Nike is revolutionizing the way the upper fabric is manufactured. Nike’s Flyprint is the first 3D printed textile upper for performance footwear.
Using a proprietary variant of the popular FDM 3D printing technology named as Solid Deposit Modeling (SDM), Nike is focusing its expertise on fabricating lightweight shoes. The technology uses a flexible filament TPU to print the upper fabric.
The Nike Flyprint method starts with capturing the athlete data. This data records how the athlete runs and uses their feet. This data is then transported to computational designing software to appropriately design the material composition. This formulated data is then utilized by the SDM 3D printer to print the flexible upper fabric.
The fabric can be so structured that individual lines can be adjusted locally without affecting the global structure. This helps in location-specific rigidity & slackness. 3D printing the fabric also allows unique weaving designs to allow more breathing design, while still being lightweight.
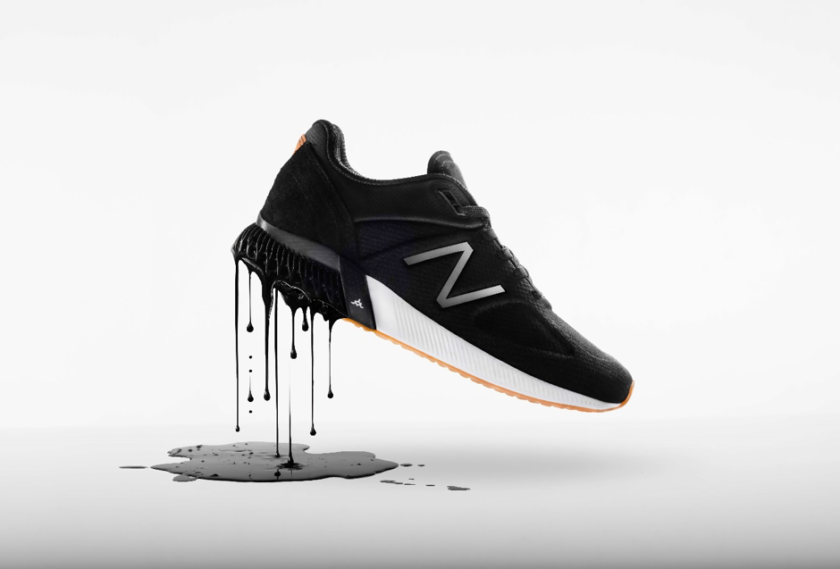
New Balance TripleCell

Source: Formlabs
In 2017, New Balance partnered with Formlabs to develop a system of 3D printing performance-optimized shoes that focused on providing higher durability than the traditionally manufactured shoes.
Formlabs engineers researched & developed a new material – Rebound Resin for New Balance to accommodate their stringent requirements of energy return and elasticity. This new material will replace the traditionally used EVA material for the shoe sole.
The shoes will be 3D printed via a technology platform called TripleCell powered by Formlabs’ Low Force Stereolithography (LFS) 3D printers. The process is similar to regular SLA 3D printing but it reduces the forces exerted on parts during the print process. The platform will print the entire sole as a single piece instead of different pieces being glued together.
Just recently, New Balance and Formlabs expanded on its commitment to continuous innovation and announced the launch of FuelCell Echo Triple. The new shoe will also be a part of the same manufacturing platform using the same material.
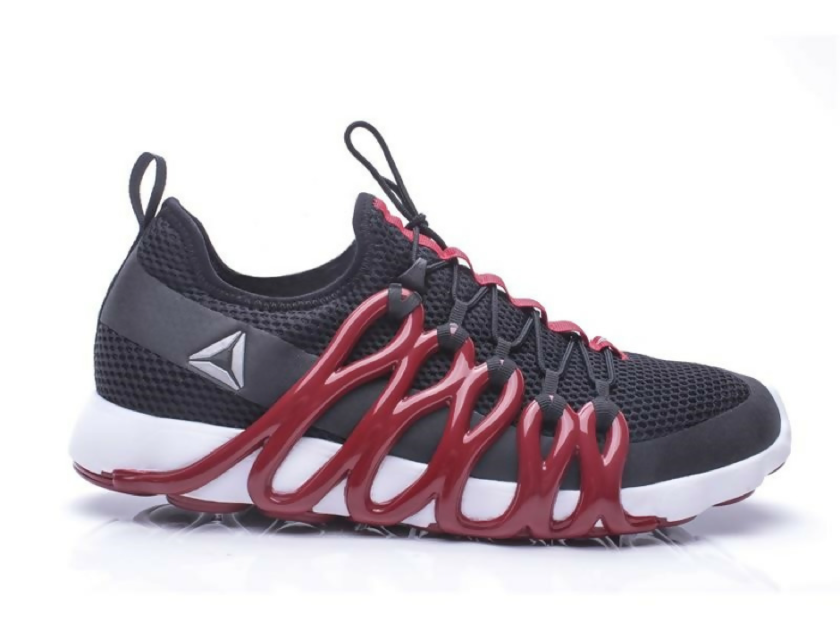
Reebok Liquid Factory

Source: Reebok
As early as 2016, Reebok industries launched its innovative manufacturing innovation – Liquid Factory. The Reebok team developed a process that used state-of-the-art software coupled with robotics to literally draw the shoes; a process best described as 3D Drawing, rather than manufacturing.
The essence of the process lies in the new proprietary liquid material developed by its partner BASF. The process eliminates the use of molds to precisely 3D print the shoe in the material which is deposited in layers in a unique geometry.
The shoe is aesthetically appealing and is made to deliver high-performance. This shoe also focused on an energy-return shoe. According to the Reebok team, the most exciting achievement of the Liquid factory is the speed at which the shoe could be manufactured. A speed never imagined before.
Groundbreaking Transformations in the Footwear Industry
The footwear industry is an inventory-heavy industry with the need for manufacturing shoes in multiple sizes, colors, and styles for each gender. This landscape is also changing with 3D printing.
Industry leaders like Adidas, Nike, New Balance, & Reebok are all manufacturing 3D printed footwear in different methods. They have pioneered a new way to manufacture footwear traditionally manufactured through molds.
Their initiatives have taken the 3D printing applications from the prototyping stage to the scale manufacturing stage to transform the footwear industry. For the footwear industry, the digital manufacturing revolution has arrived.


